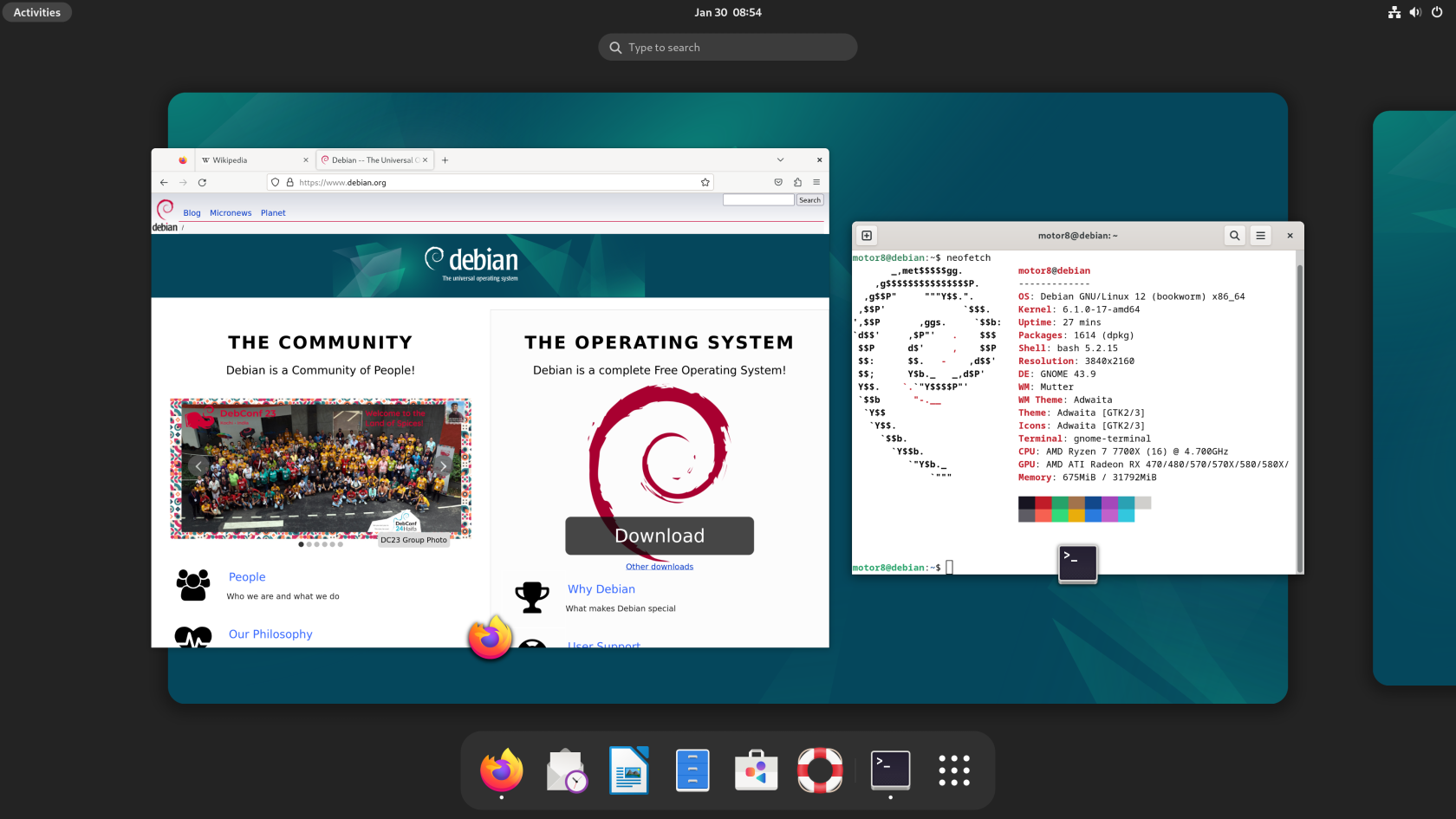
What is Linux?
The Linux kernel is the core of the operating system that facilitates between software and hardware. The kernel is packaged alongside software created by other open-source developers into a 'distro' – or a distribution.
Entire Linux distros can derive from other distros and create a family tree. Debian is root of Ubuntu which is used in turn for Raspberry Pi OS, ElementaryOS, Linux Mint and many others.
Bootloader
Terminal or Console
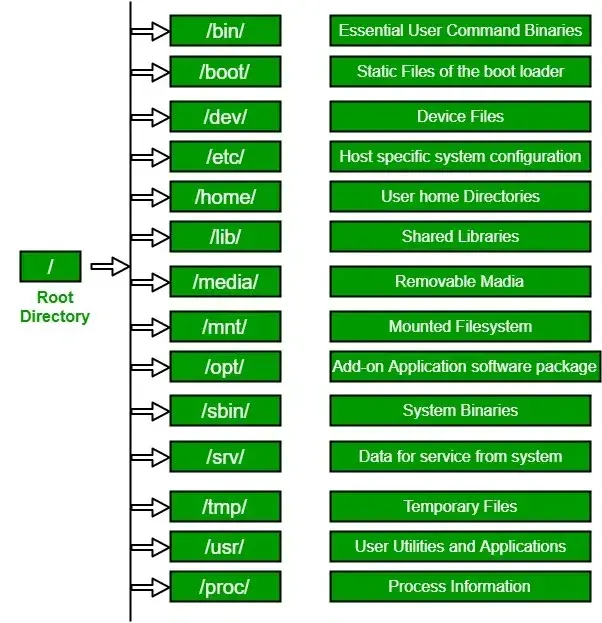
Filesystem
The Windows ecosystem assigns attached storage disks with a letter classification and mounts them as independent entities. This results in file paths like "C:\Users\".
Instead, Linux has the design philosophy that everything is a file meaning that all hard drives are mounted as a folder containing the files on your drive. On Linux, file paths can be expressed by their folder hierarchy. For example, user data is stored at the base of the hard drive within a folder named home, e.g. "/home/username".
Desktop Environment
Debian uses GNOME by default, but other common desktop environments include:
Software freedom and equitable access are central tenets of many Linux distributions. The decentralized development process is enabled by the open-source ethos of open knowledge sharing and peer participation. Much of our modern world is powered through open-source software projects, such as openssl which acts as the backbone of the internet.