Domains & URLs
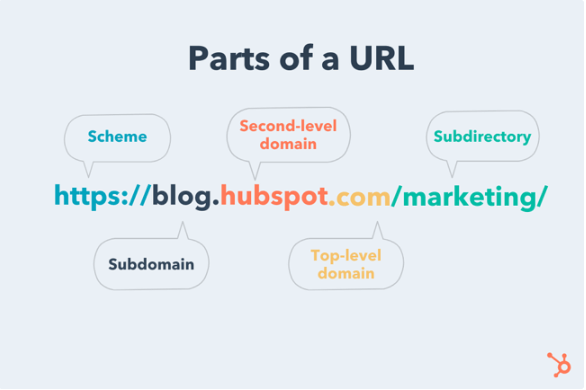
A full web domain URL might be https://www.example.com.
Domain names are used to identify autonomous areas of the World Wide Web under the control of a person, corporation or other entity. These are used for gaining access to websites, email and other services. Web domains are listed on the Domain Name System – a distributed registry to help locate servers around the globe.
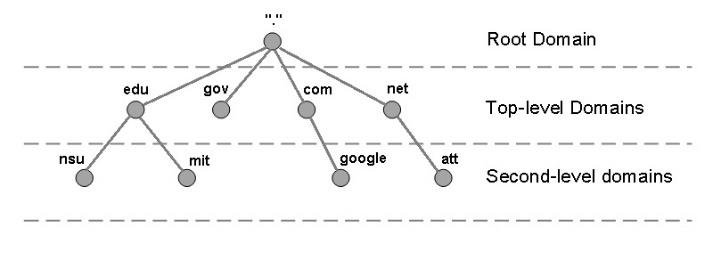
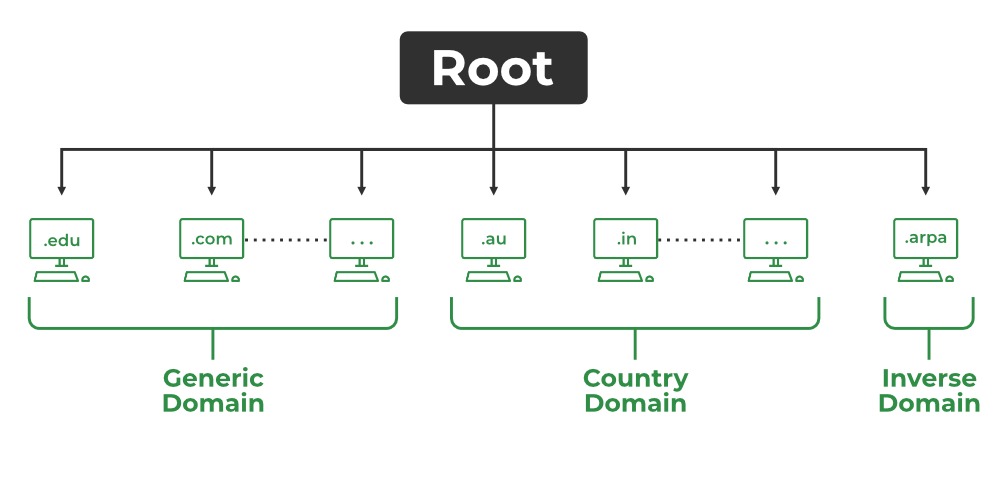
Much like the file system on the Linux operating system, Web addresses start from a root that contains all domains. Stemming from the root, there are top-level domains like the popular .com, .info, .net, .edu, and .org. There are also special country code web domains, as well as the recently expanded purpose-specific domains – such as .news, .tech, .name or .blue.
These "TLDs" are carefully maintained by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) – a global non-profit that handles the development of policies and procedures for the Domain Name System.
Second-level domains offer personality and customization to a URL. They are combined with a top-level domain using a period to create a full web domain name. When purchasing a domain name, you are generally renting access to this specific combination of top- and second-level domain for a pre-determined period of time.
Domain registrars often provide discounts for the first year, but following years come with higher annual renewal fees.
Single Domain
For many people, you will probably only require one domain name. We will be using SWAG to connect our server to the World Wide Web and this project is configured to use a single domain with sub-domains as a default.
Sub-Domains
When offering multiple independent services from your server – such as OwnCloud or Radarr – we can use sub-domains to separate these web applications into different URLs.
Using this example, radarr.example.com could direct you to the Radarr web application.
These are an excellent way to build a digital community and brand identity around the same domain name. With this technique, we could host a primary website at example.com, as well as a Flarum forum at forum.example.com and a WordPress blog available at blog.example.com.
Multiple Domains
SWAG can configured to act as the access point for multiple different web domain names – such as example.com and example.org. This makes it so you can run a personal and professional web domain from home using the same server.
Each of these domains will be listed under the same SSL certificate and therefore linked.